How to Install EF Core
DBContext in Entity Framework Core
What is DBSet in EF Core
What is Migrations in EF Core
LINQ to Entities in Entity Framework Core
Seeding data in Entity Framework Core
Lazy loading and Eager Loading are not same in EF Core
Explicit loading in EF Core
Entity States in EF Core

How to seed data in Entity Framework Core 2026?
Seed data in EntityFrameworkCore:-
This article explains how to seed data in entity framework core.It means automatically inserting initial data or default data into database, when it is created or migrated.
For example, very first time you are going to use an application,at that time i need data in login table to be loaded automatically for admin user.
Where Seeding data in EntityFrameworkCore commonly used:-
- Default Users(eg:-Admin account)
- Lookup tables(Roles,States,Countries)
- Demo or test data
- if reference data is required for app to work.
Two types of Seeding in EntityFrameworkCore:-
-Model based seeding(Migration)
-Runtime seeding(startup)
Model based seeding:-
Here we need to override onModelCreating method of dbcontext class and use HasData method to specify initial data for each entity like Roles,user,etc
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity
().HasData(
new Role { Id = 1, Description = "Admin" },
new Role { Id = 2, Description = "User" }
);
}
Runtime Seeding:-
It is nothing but populating the database with initial data using application logic,rather than migration.
Step 1: Create AppDBContext.cs
public class AppDBContext : DbContext
{
public string ConnectionString { get; set; }
public DbSet Users { get; set; }
public DbSet Roles { get; set; }
public AppDBContext(DbContextOptions options)
: base(options)
{
Debug.WriteLine("AppDbContext created");
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
Console.WriteLine("OnModelCreating executed");
modelBuilder.Entity
().HasData(
new Roles { Id = 1, Description = "Admin",CreatedAt="12-01-2026",UpdatedAt = new DateTime(2026, 1, 12).ToString(), },
new Roles { Id = 2, Description = "User", CreatedAt = "12-01-2026", UpdatedAt = new DateTime(2026, 1, 12).ToString(), }
);
}
}
Step 2: Create DBSeeder class
public static class DbSeeder
{
public static async Task SeedAsync(AppDBContext context)
{
if (!context.Roles.Any())
{
context.Roles.AddRange(
new Roles
{
// Id = 1,
Description = "Admin",
CreatedAt = DateTime.UtcNow.ToString(),
UpdatedAt = DateTime.UtcNow.ToString()
},
new Roles
{
// Id = 2,
Description = "User",
CreatedAt = DateTime.UtcNow.ToString(),
UpdatedAt = DateTime.UtcNow.ToString()
}
);
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
}
}
Step 3: Now call this Dbseeder class in Program.cs
using var scope=serviceprovider.CreateScope();
var context=scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService();
await DbSeeder.SeedAsync(context);
var count=context.Roles.Count();
Debug.WriteLine(count);
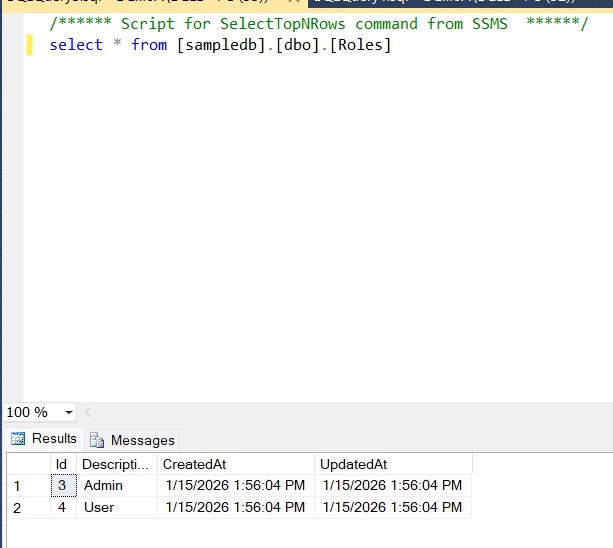
Output:-